The Blue Screen of Death (BSOD), also known as a stop error, is a dreaded sight for any Windows user. It signals a critical system failure, forcing your computer to abruptly halt. While alarming, understanding the causes and troubleshooting steps can help you resolve these issues and prevent future occurrences. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down the BSOD, explain common error codes, and provide practical solutions to get your system back on track.
What is the Blue Screen of Death?
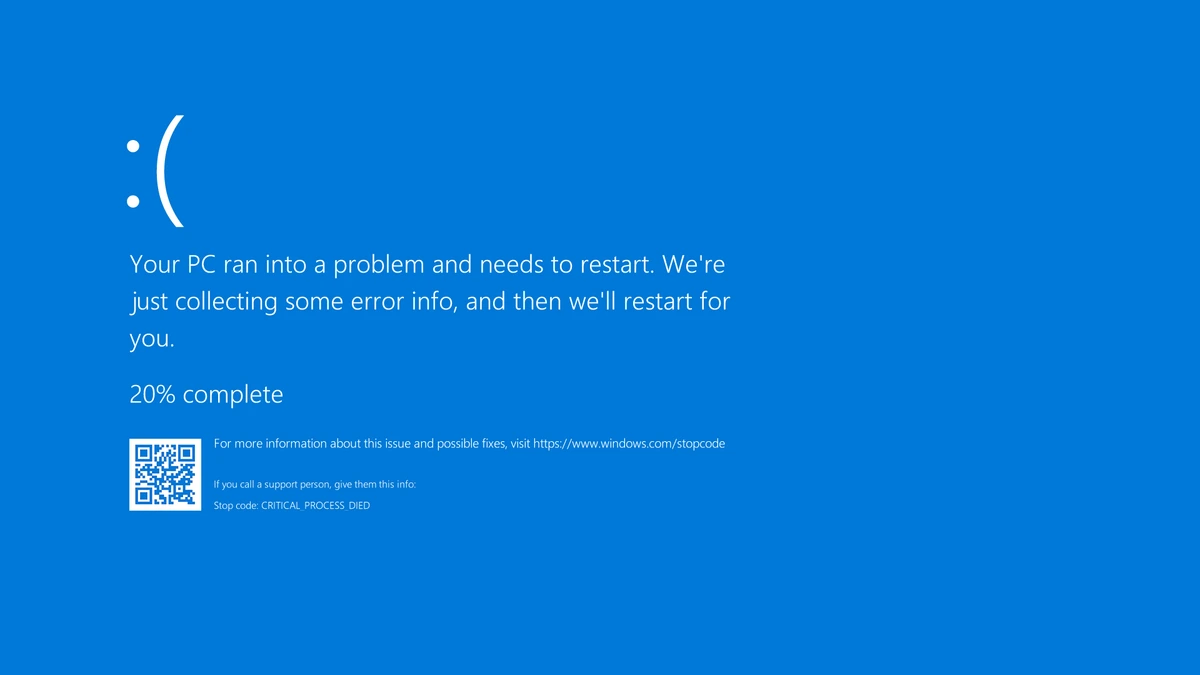
The BSOD is a safeguard implemented by Windows to prevent further damage when a critical error occurs. It displays a blue screen with an error message, often accompanied by a stop code or bug check code. This code provides crucial information about the nature of the failure.
Common BSOD Error Codes and Their Meanings:
- STOP 0x0000007E (SYSTEM_THREAD_EXCEPTION_NOT_HANDLED): Indicates a driver or hardware issue.
- STOP 0x000000A (IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL): Often points to driver incompatibility or memory problems.
- STOP 0x0000001E (KMODE_EXCEPTION_NOT_HANDLED): Similar to 7E, suggests driver or hardware issues.
- STOP 0x00000050 (PAGE_FAULT_IN_NONPAGED_AREA): Indicates a memory error, faulty driver, or corrupted file system.
- STOP 0x00000124 (WHEA_UNCORRECTABLE_ERROR): Often related to hardware failure, especially CPU or memory.
- STOP 0x000000D1 (DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL): Problem with a device driver.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Note the Error Code: The stop code is crucial for diagnosing the problem.
- Restart Your Computer: A simple restart can sometimes resolve temporary glitches.
- Check for Recent Hardware or Software Changes: Uninstall any recently installed drivers or software.
- Update Drivers: Outdated or corrupted drivers are a common cause of BSODs.
- Run Windows Memory Diagnostic: Test your RAM for errors.
- Check Hard Drive for Errors: Use CHKDSK to scan and repair file system issues.
- Run System File Checker (SFC): Repair corrupted system files.
- Perform a System Restore: Revert your system to a previous working state.
- Check for Overheating: Ensure your computer’s cooling system is functioning properly.
- Reinstall Windows (Last Resort): If all else fails, a clean install of Windows may be necessary.
Prevention Tips:
- Keep your operating system and drivers up to date.
- Install software from trusted sources.
- Use reliable antivirus and anti-malware software.
- Ensure adequate ventilation for your computer.
- Regularly back up your data.
BSOD Driver Errors: Identifying and Fixing Driver-Related Blue Screens
Driver issues are a frequent culprit behind the dreaded Blue Screen of Death (BSOD). When a driver conflicts with the operating system or other hardware, it can lead to system instability and crashes. This article focuses on identifying and fixing driver-related BSOD errors, providing detailed troubleshooting steps and best practices.
Identifying Driver-Related BSODs:
- Error Codes: Common driver-related stop codes include IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL (0xA), SYSTEM_THREAD_EXCEPTION_NOT_HANDLED (0x7E), and DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL (0xD1).
- Recent Driver Updates: If the BSOD started after a driver update, the new driver is likely the cause.
- Device Manager: Check Device Manager for any devices with yellow exclamation marks, indicating driver problems.
- Event Viewer: Examine the Event Viewer for driver-related error messages.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Roll Back Drivers: If the BSOD started after a driver update, roll back to the previous driver version.
- pdate Drivers: Ensure you have the latest drivers from the manufacturer’s website.
- Uninstall and Reinstall Drivers: Completely remove and reinstall the driver to eliminate corruption.
- Disable Problematic Devices: Temporarily disable devices suspected of causing the BSOD to isolate the issue.
- Use Driver Verifier: This Windows tool can help identify problematic drivers by stressing them. Be careful using this tool, as it can cause frequent BSOD’s.
- Check for Driver Compatibility: Ensure the drivers are compatible with your operating system.
Best Practices for Driver Management:
- Download drivers from the manufacturer’s website.
- Avoid using third-party driver update tools.
- Create system restore points before installing new drivers.
- Regularly check for driver updates.
BSOD Memory Errors: Diagnosing and Resolving RAM-Related Blue Screens
Faulty or incompatible RAM can lead to BSOD errors, causing system instability and data loss. This article delves into the diagnosis and resolution of memory-related BSODs, providing detailed troubleshooting steps and best practices for RAM management.
Identifying Memory-Related BSODs:
- Error Codes: Common memory-related stop codes include PAGE_FAULT_IN_NONPAGED_AREA (0x50) and WHEA_UNCORRECTABLE_ERROR (0x124).
- System Instability: Frequent crashes, freezes, and unexpected restarts can indicate memory problems.
- Memory Diagnostic Tool: Windows includes a built-in Memory Diagnostic tool to test RAM for errors.
Troubleshooting Steps:
- Run Windows Memory Diagnostic: Use the built-in tool to scan your RAM for errors.
- Check RAM Compatibility: Ensure your RAM modules are compatible with your motherboard.
- Reseat RAM Modules: Remove and reinsert the RAM modules to ensure proper connection.
- Test RAM Modules Individually: Remove all but one RAM module and test each module separately.
- Replace Faulty RAM: If a RAM module is found to be faulty, replace it with a new one.
- Check RAM Speed and Timings: Ensure your RAM is running at the correct speed and timings in the BIOS.
Best Practices for RAM Management:
- Use high-quality RAM modules from reputable manufacturers.
- Ensure proper RAM cooling.
- Avoid overclocking RAM beyond its rated specifications.
- Regularly check for BIOS updates.
By providing in-depth information and actionable advice, these articles can help users effectively troubleshoot and resolve BSOD errors, improving their overall computing experience.
Conclusion:
While the BSOD can be intimidating, a systematic approach to troubleshooting can help you identify and resolve the underlying issues. By understanding the common error codes and following the recommended steps, you can minimize the impact of BSOD errors and keep your system running smoothly.